▲圖片來源:dataconomy
With the average data breach cost exceeding $4.35 million, 2022 is expected to break all previous records for enterprise breaches globally. That is 12.7 % more expensive than the $3.86 million average data breach cost in 2020. It was also discovered that a record 83% of businesses reported multiple breaches and that it takes 277 days on average to discover a breach. Enterprises must therefore examine their cybersecurity tech stacks to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
THE IBM REPORT PUTS CYBERSECURITY RISKS UNDER THE SPOTLIGHT
An effective place to start is by tightening security surrounding identity management and privileged access credentials. More businesses need to adopt identity definitions as the new security perimeter. According to IBM’s report, privileged credentials have been compromised in 19% of all breaches. The average duration of breaches brought on by stolen credentials was 327 days. The Dark Web’s best-selling privileged access credentials are in high demand for access to the IT infrastructure of financial services.

▲圖片來源:dataconomy
The report also demonstrates businesses’ reliance on implicit confidence in their overall IT infrastructure and security tech stacks. Identity and access management (IAM), privileged access management (PAM), and cloud security flaws make costly breaches possible. When zero trust can cut typical breach losses by almost $1 million, 79% of critical infrastructure firms didn’t implement one.
To lower the frequency of breaches, businesses must view implicit trust as the open back door that gives hackers access to their systems, passwords, and most sensitive confidential information. In addition, we recommend checking cybersecurity practices to stay safe against today’s digital perils.
KEY TAKEAWAYS FOR ENTERPRISES
The size of the expanding cybersecurity gap in healthcare is also quantified in the paper. According to IBM’s analysis, the average cost of a healthcare data breach is now estimated to be $10.1 million, setting a new record and surpassing last year’s $9.23 million figure by almost $1 million. The average breach cost in healthcare has been the highest for twelve years, rising 41.6 % since 2020.
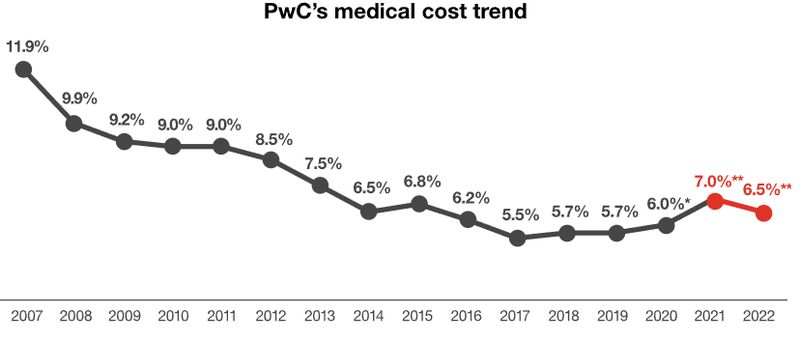
According to the data, as runaway costs are putting financial strain on businesses and customers worldwide, the cost of breaches is increasing at an inflationary rate, adding gasoline to the fire. Sixty percent of the businesses participating in IBM’s study claim that they increased their product and service costs due to the breach. At the same time, supply chain interruptions, the Ukrainian conflict, and the weak demand for goods persist. Consumers are already struggling when it comes to paying for healthcare expenses. The latest PwC report expects costs to rise by 6.5% in 2022.
▲圖片來源:dataconomy)
The IBM study also discovered that 12 to 24 months after a breach, approximately 30% of costs are still incurred, resulting in enduring price hikes for consumers.
“It is clear that cyberattacks are evolving into market stressors that are triggering chain reactions, [and] we see that these breaches are contributing to those inflationary pressures,” explained the head of strategy for IBM Security’s X-Force research team, John Hendley.
Prioritizing these three areas can help healthcare providers with tight cybersecurity budgets lower the cost of a breach while advancing zero-trust initiatives. A practical zero-trust architecture must have identity access management (IAM) that is effective, flexible, and protects both machine and human identities.

▲圖片來源:dataconomy
內文
轉貼自: dataconomy.com
若喜歡本文,請關注我們的臉書 Please Like our Facebook Page: Big Data In Finance

留下你的回應
以訪客張貼回應